In this COVID crisis, one of the most important issues came forward is the scarcity of oxygen cylinders in the hospitals. As we all knew, oxygen is the most important gas because of which survival is possible. In case of patients suffering from any kind of pulmonary disease or in different medical conditions artificial oxygen is supplied in the body of the patient to provide sufficient oxygen to different body cells. Apart from oxygen cylinders as a source for providing oxygen to patients, another term which we came across now days is an Oxygen Concentrator.
Earlier, generally people only aware about oxygen cylinders as a source for providing oxygen to a patient but during COVID, due to increase in demand of artificial oxygen supply for a patient, we all came to know about oxygen concentrators that can also provide oxygen supply to a patient in order to fulfill the required amount of oxygen in a patient’s body. Apart from this liquid oxygen is also used as medical oxygen.
Let’s try to know about different types of oxygen delivery devices available and mechanism behind them to fulfill the increasing demand of medical oxygen.
Oxygen concentrator
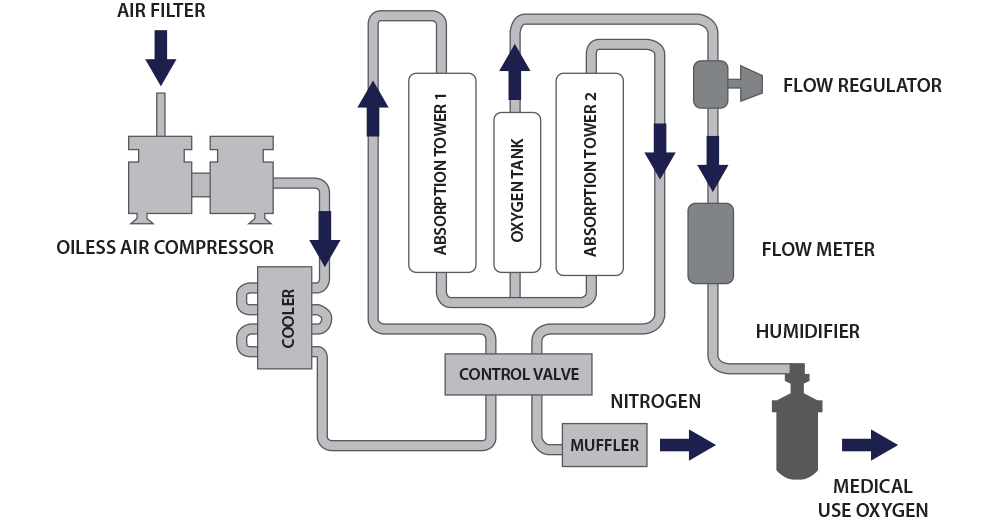
“Oxygen concentrator” or “Oxygen generator” is a device that can generate pure medical oxygen which can be provided to the patient in conditions of lower levels of oxygen saturation in order to avoid extra pressure on lungs to get in sufficient amount of oxygen required. In conditions of lower oxygen saturation SpO2 approximately 88 to 92, oxygen concentrators are good enough to provide oxygen enriched air. It can provide up to 5-10 liters of oxygen per minute which is appropriate in less severe cases.
The key features of oxygen concentrators are they does not requires refilling as it produces oxygen by extracting it from air and removing nitrogen . They can provide infinite amount of pure medical oxygen as long as they are connected to a power supply or battery. As we all know, in COVID situations doctors are recommending to use oxygen concentrators at home so as to avoid any fatalities in patients with low severity. These are portable, cost effective, long term use devices and also it eliminates the risk of leakage as it produces oxygen when it is plugged in to a power supply, so these are safe enough to be operated at home.
If we talk about the disadvantages then the filters need to be replaced after a considerable time period to maintain the purity of the oxygen to be supplied. It requires a power supply to be operated and there should always be a battery backup in order to avoid any risk to the life of the patients. The moisture content in the surrounding air could be a cause of interference with the production of pure oxygen.
Working mechanism:
The device comprise of a compressor, sieve filters inside a cabinet, tubing and nasal cannula. Require to be plugged in to a power supply to get started. The concentrator draws in air from the surroundings which could be consisted of dust particles, bacteria and other particulates, these are removed by passing through a series of filters. Then the air is forced by compressor to the canisters consisting of two molecular sieve beds. These sieve beds comprises of Zeolite (Aluminium silicate). The sieve bed adsorbs nitrogen from the air, leaving concentrated oxygen up to 90 – 95% pure and in the other sieve bed it is desorbed and exhausted in surrounding. The oxygen outflow from one sieve bed coincides with nitrogen discharge in the other thus maintaining a continuous oxygen flow to be supplied to the storage vessel to be available to the patient via mask or nasal cannula.
Compressed oxygen cylinders
Oxygen cylinder contains compressed oxygen gas in metal containers under high pressure, which can provide oxygen to the patients facing severe pulmonary distress. Oxygen cylinders are the most common type of medical grade oxygen providing system known to people and are available in different sizes based on the amount of oxygen needed. One can manage the amount of oxygen to be given to the patient by regulating the knob in moderate and severe pateints.
The main issue with these cylinders is that they provide continuous oxygen supply and requires refilling once it goes off and includes extra charges of transportation. These are heavy, difficult to carry, needs to be checked regularly for any leakage.
Working mechanism:
At the top of the cylinder a regulator is attached which allows adjustment of oxygen flow rate required by the patient. The tap is connected to the delivery device through a tube with nasal cannula. A barometer is attached to the cylinder for monitoring of the amount of oxygen available in the cylinder for supply.
Liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen is a cryogenic liquefied gas with boiling point of -183°C. Liquid oxygen is stored and transported in highly insulated containers so as to avoid any accidental spillage or injury. Liquefied form of oxygen provides larger volume of oxygen to be stored over gaseous form and also it is lighter to be carried and transported than oxygen in gaseous form. As a large volume of oxygen can be stored when it is liquefied therefore it is more favored as it runs for longer time duration. Care should be taken while handling liquefied oxygen because its contact can cause severe eye and skin irritation and frostbite.
Working mechanism:
One of the most common methods of producing liquid oxygen is separating oxygen in Air Separation Units. Liquid oxygen is produced by cooling the atmospheric air in order to liquefy it. The different gases liquefy at different temperatures to get in pure liquid oxygen at a particular temperature fractionally distilling different gases. This liquid oxygen is then passed through another distillation process so as to remove any other component present so that it is purified enough to be used in medical grade oxygen systems. This liquefied oxygen is then stored in containers or tanks so as to make it available to hospitals.
These are different oxygen delivery systems which are used in medical grounds so as to prevent any fatality due to lack of oxygen to the patients facing any kind of respiratory distress. These oxygen supplying systems can be used on the basis of the degree of severity and underlying medical condition of the patient. Each system has its own pros and cons but safer handling and following the precautionary measurements these can be used as life savior for those with pulmonary diseases.
Blog By – Manisha Sharma
Related posts
Subscribe
* You will receive the latest news and updates on your favorite celebrities!